Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
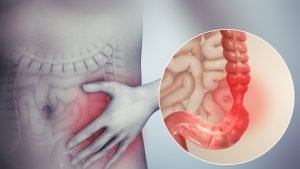
Irritable bowel syndrome is a problem experienced by many people that affects the large intestine. Not all people have signs and symptoms as they can control them by managing diet, stress, and lifestyle. However, others have symptoms like bloating, abdominal pain, cramping, constipation, or diarrhea, which needs to be managed for quite some time. In others, the bowel movement changes in appearance, while others change how often they have bowel movements (Varjú, Farkas, Hegyi, Garami, Szabó, et al., 2017).
Sometimes the IBS becomes more persistent to the point of seeing a doctor as they may indicate a sign of more severe conditions like cancer. Such symptoms include night diarrhea, weight loss, experiencing bleeding, which is a symptom of severe conditions like anal fissures, hemorrhoids, and inflammatory bowel diseases. Other serious signs include unexplained vomiting, having difficulties swallowing, and persistent pain that isn’t relieved by bowel movements or gas.
IBS is caused mainly by intestinal muscle contraction, whereby if they are more robust and last longer than usual, they can cause bloating and diarrhea. Also, when the intestinal contractions are weaker, they slow down food passage leading to hard and dry stool, causing bleeding. Abnormalities in the nervous digestion system can cause poor coordination between the intestines and the brain, leading to an overreaction in the normal digestion process, which in return causes abdominal discomforts when passing gas or stool. These abnormalities cause pain, diarrhea, and constipation.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome can also be caused by severe infections caused by bacteria or viruses, spreading to the large intestines. People who have experienced a lot of stress, especially during childhood, tend to have Irritable Bowel Syndrome symptoms. Also, the intestines have viruses that lay a crucial role in people’s health. Changes in those gut microbes can cause IBS.
There is no proven treatment for Irritable Bowel Syndrome. However, medications manage and relieve the symptoms (Moayyedi, Andrews, MacQueen, Korownyk, Marsiglio, et al., 2019). Most home remedies for controlling IBS include physical exercise, eating smaller meals, minimizing stress, avoiding spicy and deep-fried foods, and taking probiotics to relieve gas. However, if the problem persists, some medication can help relieve the problem, including Alosetron, which slows the waste movements and relaxes the colon. Eluxadoline, Rifaximin, Lubiprostone, and Linaclotide are used to control muscle spasms, constipation and ease pain.
Summary
Symptoms
- Cramping and abdominal pains related to abnormal passing bowel movement
- Different bowel movement appearance
- Changes in bowel movement occasions
- Night diarrhea, weight loss, and bleeding during bowel movements
- Unexplained vomiting, difficulties swallowing, and persistent abdominal pain.
Causes
- Contractions of muscles in the intestine.
- Nervous system abnormalities
- Severe bacterial infection
- Continuous exposure to stress.
- Changes in bacteria’s found in the intestines.
Treatment
- Home remedies include participation in regular exercises, consuming smaller meals, avoiding spicy foods, minimizing stress, and taking probiotics.
- Hospital medication to relieve the disease includes Eluxadoline, Rifaximin, Lubiprostone, Linaclotide, and Alosetron used to control muscle spasms, constipation, and ease pain.

